Layer Options and Meanings |

|

|
|
Layer Options and Meanings |

|

|
|
|
||
In SnapMaps a variety of layers can be turned on and off. Each layer provides a different piece of information. Multiple layers can be active at one time. The images will be stacked on top of each other in a specific order: the first active layer in the list will be drawn on the bottom, then the next one on the list drawn on top of it, and so on. For example, if you have "Aerial" and "5 ft Contours" both checked, the contours will be drawn on top of the aerial image. Many of the layers are semi-transparent so that they may be used together.
The Layers sidebar is used to toggle the visibility of each layer. The layer side bar can be resized by dragging its edge or corner. Check a box to display that layer. If you want to turn on all of the layers in a section, check the Turn on/off all checkbox next to the layer title. To turn them all off uncheck the box. You may have to click this twice to get the result you desire.You can use the ![]() or
or ![]() buttons to collapse the sidebar.
buttons to collapse the sidebar.
Each layer also has an opacity slider ![]() that controls its transparency.
that controls its transparency.
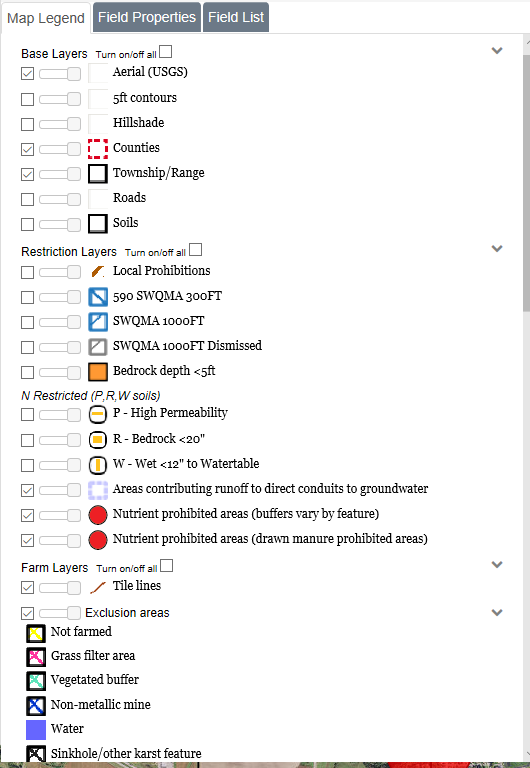
•Aerial: Aerial map with high quality color photos of the state up to around the 50ft scale. This layer is from an external source. At times this source may not load correctly, and instead of the aerial map, nothing or a checkerboard pattern may be loaded. This is usually temporary, and may not affect all scales. Zoom in to see if the layer loads properly, otherwise simply turn the layer off.
•5ft Contours: At the 2000ft scale and above this layer shows the terrain shading. At scales smaller than 2000ft this layer shows the 5ft contours. See Using the 5ft Contours for more information.
•Hillshade: Is a 3D representation of the surface. This can help with determining where water will drain off a field.
•Counties: Highlights the county borders in a dashed red line. In the middle a label with the county name is drawn.
•Township and Range: At the 5000ft scale and below this layer highlights the borders of each township in black. In the middle a label with the range, direction, and section is drawn.
•Roads: Overlays road information on the map, including the Aerial layer. When zoomed out, only major roads can be seen. Zoom in to see local roads. Note: Sometimes the road labels can be covered by the Layers sidebar or other on screen elements.
•Soils: At the 1000ft scale and below this layer highlights soil borders and displays the soil's "map unit". Sometimes this label can be hard to find; use the Identify Soil Tool to quickly find it. See Using the Identify Soil Tool for more information.
•Local Prohibitions: Is limited coverage map layer that shows areas with additional winter spreading rules at the county level. Currently we only have Door and Kewaunee County data. For more information about these restrictions please contact the appropriate county office.
•590 SWQMA 300ft or CAFO SWQMA 300ft: At the 2000ft scale and below this layer will surround perennial streams, in a 300ft radius, with diagonal blue lines going from upper left to lower right. If your farm is a CAFO then intermittent streams will also be surrounded within 300ft.
•SWQMA 1000ft: At the 2000ft scale and below this layer surrounds waterbodies (lakes and ponds), in a 1000ft radius, with diagonal blue lines going from upper right to lower left.
•SWQMA 1000ft Dismissed:This layer will show any SWQMA's dismissed by the user. A user may dismiss a SWQMA if the DNR water feature layer incorrectly shows a water feature such as a manure pond as a qualifying SWQMA.
•N Restricted (P.R,W soils): At the 2000ft scale and below there are three layers with gold lines or squares for soils which have N application restrictions due to risk of nitrate leaching to groundwater. These are P- High Permeability (horizontal lines), R- Bedrock within 20 inches (squares), and W- water table within 12 inches from surface (vertical lines).
•CAFO Manure Restriction (W): This layer is only an option for CAFO (permitted) farms. At the 1000ft scale and below this layer covers soils which have a W restriction (soil may have bedrock within 24 inches of soil surface) with cyan W's.
•CAFO Manure Restrictions (R): This layer is only an option for CAFO (permitted) farms. At the 1000ft scale and below this layer covers soils which have an R restriction (soil may have water table within 24 inches of soil surface) with tan/gray R's.
•Bedrock Depth <5ft: This layer displays the areas where the bedrock is less than 5 feet.
•CAFO 200ft Downslope Buffer: This layer is only an option for CAFO (permitted) farms, Setback for solid and emergency liquid manure applications. Set back requirement is in effect where the buffer area is upslope of a direct conduit to groundwater.
•Door Cty Ord. no manure: Door County only. Please refer to the county for more information.
•Nutrient prohibited areas (automated buffers): Nutrient application prohibition automatically drawn around specific features (example: wells) according to specifications in the NRCS Nutrient Management Standard 590.
•Nutrient prohibited areas (drawn manure prohibited areas): Areas drawn in by the SnapMaps user where manure or other nutrients should not be applied
•P - High Permeabilty:
•R - Bedrock <20":
•W - Wet <12" to Watertable:
•Soil Samples: This layer allows you to view any soil sample points that are present on the map.
•Exclusion Areas: This layer displays the different types of exclusion areas shown in the Layers sidebar on each corresponding point.
•Points: This layer displays the icons shown in the Layers sidebar on each corresponding point.
•Drinking well is a private well for a household or farmstead.
•Public well is a well that serves at least 25 people for at least 6 months per year. Also known as non-community potable water wells, examples include schools, restaurants and churches.
•Irrigation well is a well used only for irrigation, never for drinking water.
•Sinkhole is a depression in the ground that has no natural external surface drainage so that rainwater or runoff entering the sinkhole typically drains to the subsurface. Sinkholes are classified in the Nutrient Management Standard 590 as direct conduits to groundwater.
•Non-metallic mine is typically a gravel pit or sand mine. Non-metallic mines are classified in the Nutrient Management Standard 590 as direct conduits to groundwater.
•Fractured bedrock at surface is classified in the Nutrient Management Standard 590 as a direct conduit to groundwater.
•Other direct conduit is any other direct conduit for water to flow from the surface to groundwater not already listed above. These include mine shafts, quarries, and depressional groundwater recharge areas over shallow fractured bedrock.
•Tile outlet locates where tile lines discharge to the soil surface or surface water.
•Tile inlet locates a surface tile inlet.
•Point Buffers: This layer surrounds point features with a transparent red nutrient nutrient prohibition buffer of the width specified in the NRCS Nutrient Management Standard 590 or WI NR243 (permitted farms only).
•Tile lines: This layer shows any tile lines drawn on the map.
•County Defined Karst Features: This layer will show any karst features that have been defined by the county the user is working in.
•Municipal Wells: This layer is a transparent red 1000ft buffer around municipal wells identified by WI DNR. Municipal wells are also known as community wells by WI DNR.
•Fields: This layer shows the geometry of the fields with black lines with a white border.
•DNR Wetland: At the 2000ft scale and below this layer covers the DNR Wetland areas in a transparent yellow-green.
•Perennial Streams: At the 5000ft scale and below this layer highlights perennial streams in blue.
•Intermittent Streams: At the 5000ft scale and below this layer highlights intermittent streams in a dashed blue line.
•Water-bodies: At the 5000ft scale and below this layer covers lakes and ponds in blue.
•HUC 8 Basins: Shows the HUC 8 basins with a dotted pink line. The names of the HUC 8 watersheds are also a black with pink outline.
•HUC 12 Watershed: Shows the HUC 12 watershed with a dotted aqua line. The names of the HUC 12 watersheds are also a black with aqua outline.
•Impaired Waters (303d): At the 2 mile scale and below this layer shows the 2016 DNR impaired waters..
•Outstanding/Exceptional Waters: At the 2 mile scale and below this layer shows the 2016 DNR outstanding /exceptional waters.
•Concentrated Flow Channels: This layer displays the different types of concentrated flow channels shown in the Layers sidebar on each corresponding point.
•Grassed waterway is a channel that has been shaped or graded and established in perennial vegetation for the stable conveyance of runoff.
•Non-eroding channel is an area where flow concentrates in the field without leading to erosion. One example is a terrace channel.
•Ephemeral erosion channel is a shallow channel caused by the convergence of overland sheet flow and rill erosion. It will often reoccur in the same place after the field is tilled.
•Ditch is a man-made channel in the field that drains surface runoff and/or groundwater, including drainage and road ditches.
•Gully is an erosion channel that cannot be crossed with ordinary farming equipment.
•Winter Restriction Slopes > 6%: At the 2000ft scale and below this layer covers slopes greater than 6% are in a transparent pink. Use the 5ft Contour layer to identify slope direction. This layer is not shown on the maps for non-permitted farms.
•Winter Restriction Slopes 6%- 12%: For permitted farms only. At the 2000ft scale and below this layer covers slopes with an incline between 6% and 12% in a transparent pink. Use the 5ft Contour layer to identify slope direction.
•No Winter App. Slope > 12%: For permitted farms only. At the 2000ft scale and below this layer covers slopes with an incline greater than 12% in an transparent red. Use the 5ft Contour layer to identify slope direction.
•Wetland 200ft Buffer: For permitted farms only. Setback for solid and emergency liquid manure applications. Set back requirement is in effect where the buffer area is upslope of wetland.
•Direct Conduit to Ground Water 300ft: Setback for solid and emergency liquid manure applications. Set back requirement is in effect where the buffer area is upslope of the conduit to groundwater.
•Well Compensation: This layer shows the areas where DNR Well Compensation funds have provided replacement water supplies for wells contaminated with livestock manure.
•Shallow Silurian: This layer displays the Silurian dolomite soil areas where Silurian bedrock is likely to be present within 5 feet of the soil surface.
•Headland Stacks: Location of manure stacking sites.
•Lower WI River Valley Prohibition Area: This data set contains a representation of where the use of atrazine is prohibited in the Lower Wisconsin River Valley.
•Atrazine Prohibition Area: This data set contains areas in Wisconsin where use of atrazine is prohibited based on well water sample results and DATCP investigations around these well sites.
•Surface lead mining
•Processing site
•Gravel pit
•Abandon mining railroad
•Borehole
•Mine shaft
![]() This button will update all winter manure prohibited ares. It is important this button is clicked after every update to display and after any changes are made. If it is not, the winter manure prohibited areas will not be updated in the SnapPlus software upon import.
This button will update all winter manure prohibited ares. It is important this button is clicked after every update to display and after any changes are made. If it is not, the winter manure prohibited areas will not be updated in the SnapPlus software upon import.
•Feb/Mar Liquid manure prohibited areas: Map layers that are labeled Well compensation and Shallow Silurian prohibit the application of liquid manure in February and March.
•Winter Manure Prohibited Areas: This changes according to the type of plan you have ( CAFO or permitted vs Non-CAFO). Manure cannot be applied to frozen and snow covered soils within these areas.
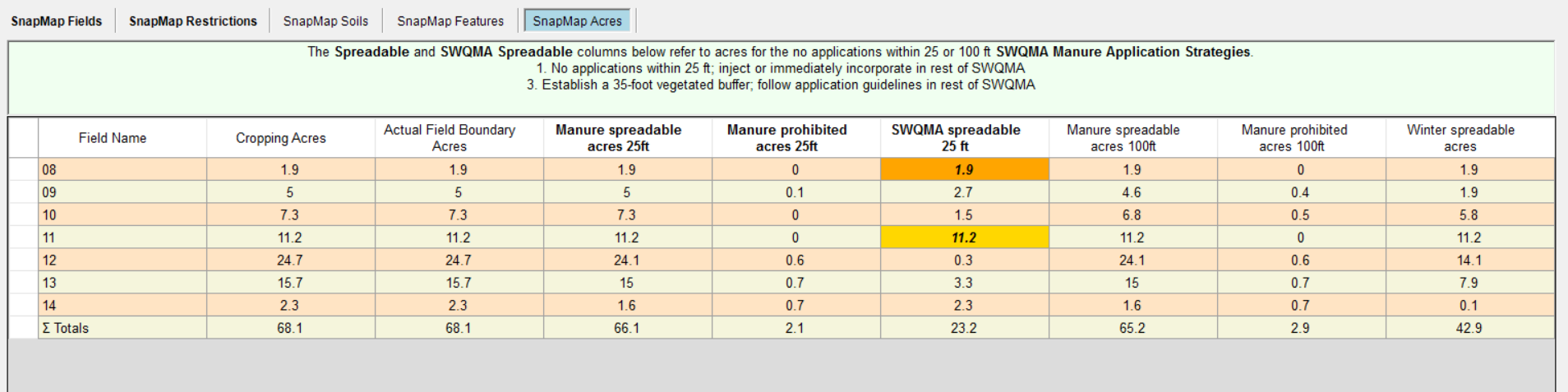 This button will update the Manure prohibited and Incorporate manure layers displayed on the maps. For fields with SWQMAs, it will map the spreading layers with either 25 ft or 100 ft manure prohibition buffers along streams and flow channels, depending on the strategy selected from the dropdown.
This button will update the Manure prohibited and Incorporate manure layers displayed on the maps. For fields with SWQMAs, it will map the spreading layers with either 25 ft or 100 ft manure prohibition buffers along streams and flow channels, depending on the strategy selected from the dropdown.
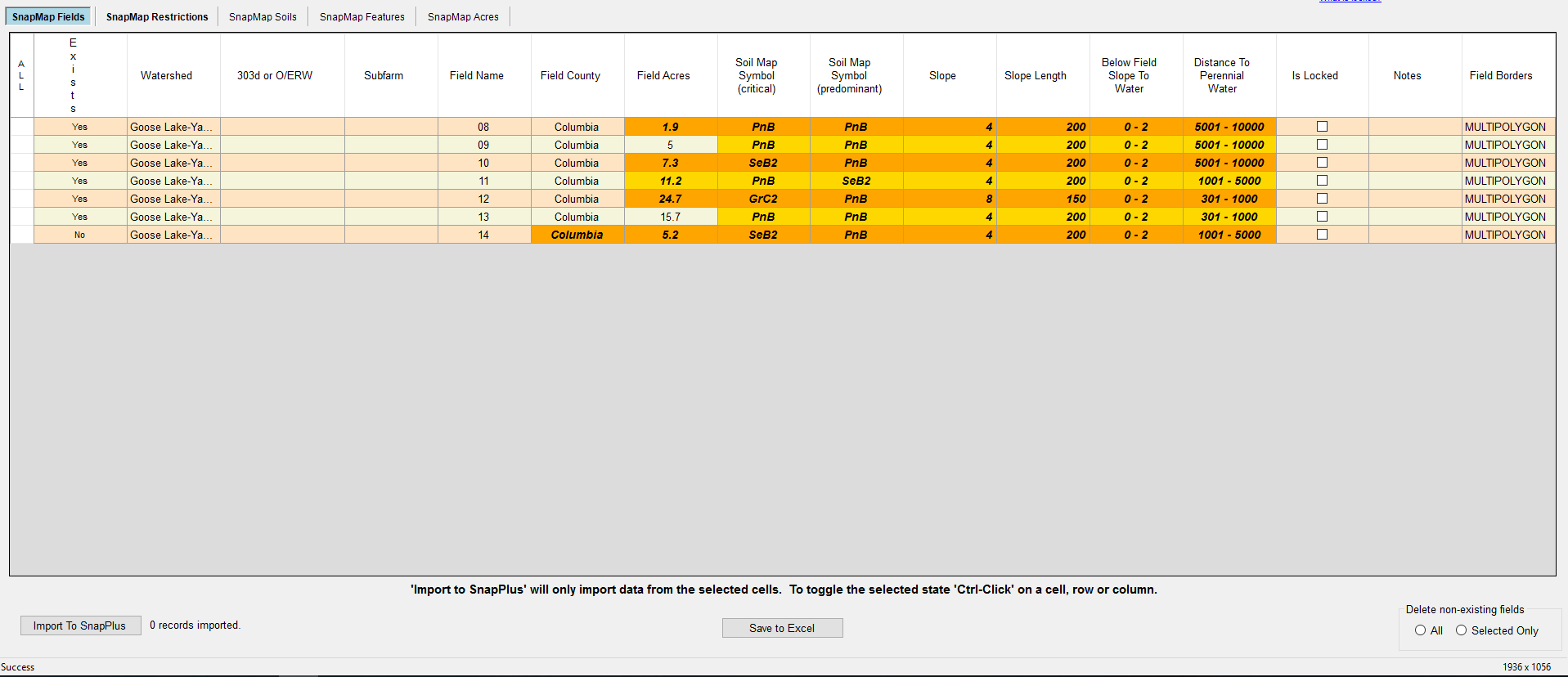
•Manure Prohibited: This layer shows where no manure may be spread.
•Incorporate manure: This layer shows the part of the SWQMA where manure has to be injected or incorporated if a 25 ft buffer is selected and the field is not long-term no-till.
These layers are found in Eastern Wisconsin where the underlying bedrock is Silurian dolomite. These areas are likely to have additional restrictions on manure applications when the proposed 2018 NR151 revisions are implemented.
•0-2ft: This layer shows where the depth to Silurian bedrock is likely to be within 2 ft. This is derived from the NRCS soil survey.
•2-5ft: This layer shows where the depth to Silurian bedrock is likely to be within 2-5 ft. This is derived from the NRCS soil survery.
•5-20ft: This layer shows where the depth to Silurian bedrock is likely to be within 20 ft. The 16 ft depth is only used in Door County because the original study identifying depth to bedrock used this depth.
•0-2ft: This layer shows where the depth to the water table over Silurian bedrock is likely to be within 0-2 ft. This is derived from the NRCS soil survey.